Malaria Vaccine Breakthrough: A New Hope for Prevention
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Malaria
Malaria continues to pose a significant threat globally, primarily due to the mosquitoes that transmit this deadly disease. These insects are considered the most perilous animals on the planet—not due to their size or strength, but because of the harmful parasites they carry. The Plasmodium genus includes four species responsible for malaria in humans, with P. falciparum being the deadliest.
When a mosquito infected with the malaria parasite bites a person, the parasite is transferred from the mosquito's saliva into the bloodstream of the new host.
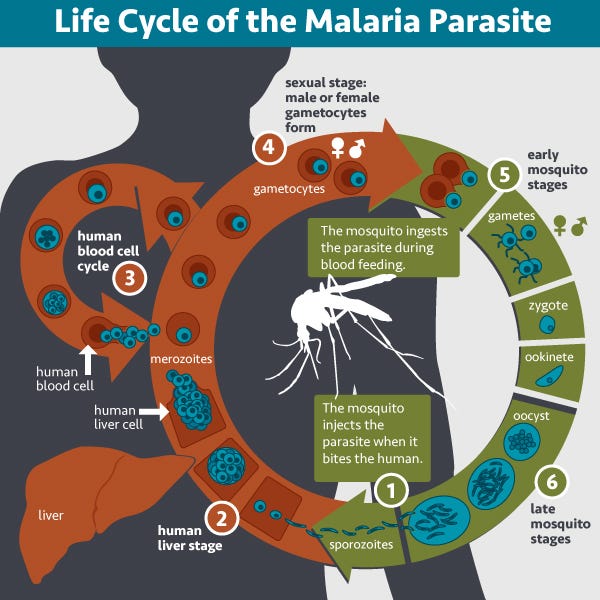
Despite the immune system's response, some parasites reach the liver, where they reproduce and transform into trophozoites. These trophozoites exit the liver and invade red blood cells, leading to further reproduction until the cells rupture, releasing new parasites into the bloodstream. This process triggers symptoms like fever, headaches, muscle aches, and nausea. In severe cases, infected blood cells may sequester in the brain, resulting in cerebral malaria, which is particularly lethal for children under five.
P. falciparum is responsible for most malaria-related deaths, with a mortality rate of about 1% in heavily impacted regions, amounting to over 400,000 fatalities annually.
Interestingly, some individuals possess the sickle cell trait, which offers a degree of protection against malaria. The sickle shape of certain blood cells tends to rupture prematurely when infected, hindering the parasite's lifecycle. However, possessing two sickle cell genes leads to sickle cell disease, which complicates malaria infection.
Currently, the most effective preventive measures against malaria include impregnated bed nets and a variety of drugs, which save numerous lives, though drug resistance is an emerging concern.
Chapter 2: A Vaccine Success
While other vaccines have recently captured public attention, a groundbreaking study has introduced a potential vaccine against malaria. This vaccine utilizes the yeast Hansenula polymorpha to express a modified form of the circumsporozoite protein, which the malaria parasite relies on to move from the mosquito gut to its salivary glands and to bind to liver cells in humans.
A clinical trial involving 450 children aged five to seventeen months in Burkina Faso assessed the vaccine's efficacy. Participants were divided into three groups: one group received the vaccine with a high dose of adjuvant, another with a low dose, and the third received a rabies vaccine as a control. The vaccination process included three doses administered four weeks apart, followed by monitoring for two weeks to six months after the final shot.
The results were promising, demonstrating 77% efficacy in the high-adjuvant group and 74% in the low-adjuvant group. Researchers are now pursuing follow-up trials to assess the vaccine's effectiveness over time and plan to conduct a phase III trial across five African sites to seek approval for a safe, affordable, and effective vaccine aimed at significantly reducing malaria's impact.
The circumsporozoite protein appears to be highly conserved among malaria strains, indicating the vaccine's potential broad applicability.
There remain unanswered questions regarding the longevity of the antibody response and other logistical considerations, such as distribution and public acceptance. However, initial participant enthusiasm suggests strong motivation to combat this deadly disease.
Overall, this advancement is a significant step forward in the battle against malaria.
This video titled "Malaria vaccine breakthrough: New cheap, option backed by WHO - BBC News" discusses the recent advancements in malaria vaccine development, shedding light on its potential to save lives.
Another video, "New malaria vaccine 'could save millions of lives' - BBC News," provides insights into the implications of the new malaria vaccine and its expected impact on global health.