Understanding VPNs: How They Operate and Protect Your Privacy
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to VPN Technology
When discussing VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, many people wonder about their function and the underlying technology. To grasp how VPNs operate, it’s essential to first understand the mechanics of the internet and how data is transmitted.

IP Address Basics
Every device that connects to the internet—be it your smartphone, tablet, smart TV, or even your smart refrigerator—has a unique identifier known as an IP address. This unique string of numbers allows each device to be recognized on the network.
For those looking to configure a VPN on their iPhone, you can find comprehensive guidelines in this article:
What is VPN Technology and VPN on iPhone?
Tech It's 2022, you've probably heard the word VPN by now. So what does it really do? VPN stands for a virtual private...
www.shakiroslann.com
Data Packets and Routing
When a device requests information, that request is transformed into a small data packet containing essential details about the device and the content it seeks. This packet travels through your Wi-Fi router, which conceals the local IP addresses under its own. It then forwards the packet to the modem, which establishes a connection to the internet via your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
The packet is routed from the modem to the nearest ISP connection point. Here, the ISP modifies the packet, assigning it a public IP address that corresponds to your general location. Importantly, this public address can be accessed by anyone on the internet.
Domain Name System (DNS) Role
The requested content resides on a server with its own IP address. The ISP plays a crucial role by locating this server, often utilizing the Domain Name System (DNS) to map the domain name (e.g., example.com) to its respective server IP addresses. This process, known as DNS lookup, is essential for ensuring that the content reaches your device.
ISP Monitoring
ISPs maintain logs that detail the domains and IP addresses you've accessed. However, if the content is served over HTTPS, the data exchanged between your device and the server is encrypted, rendering it unreadable to anyone monitoring the connection.
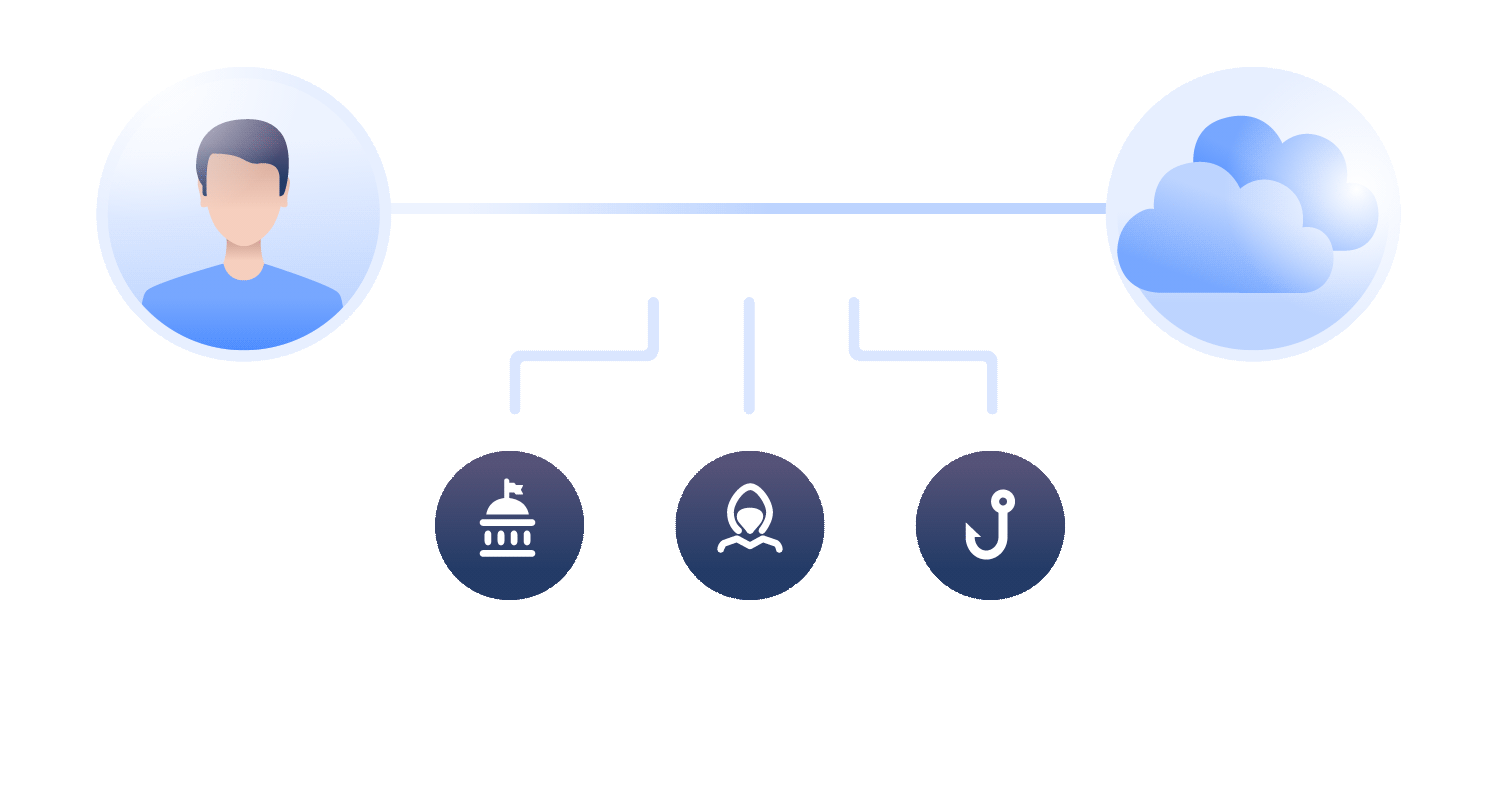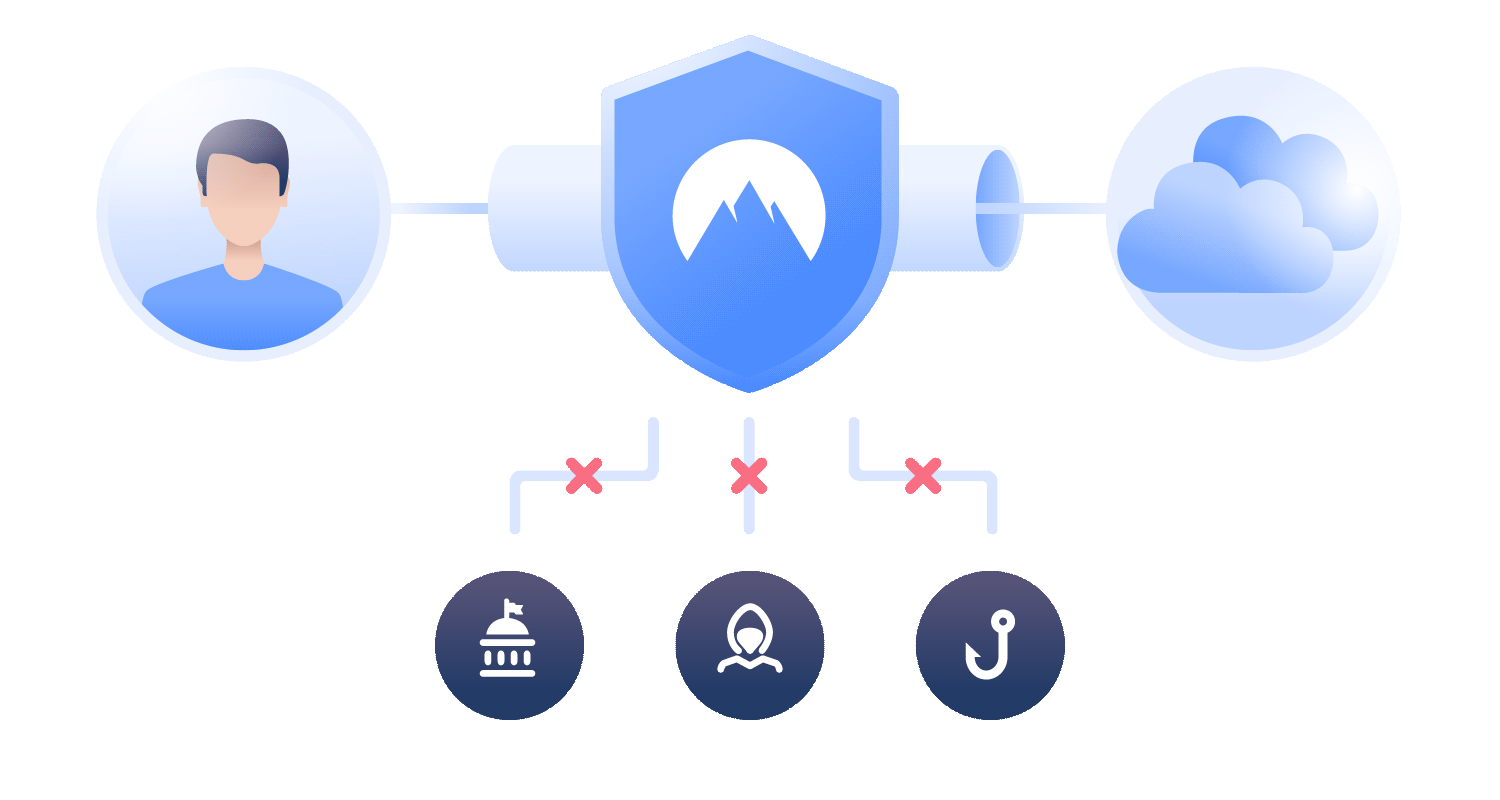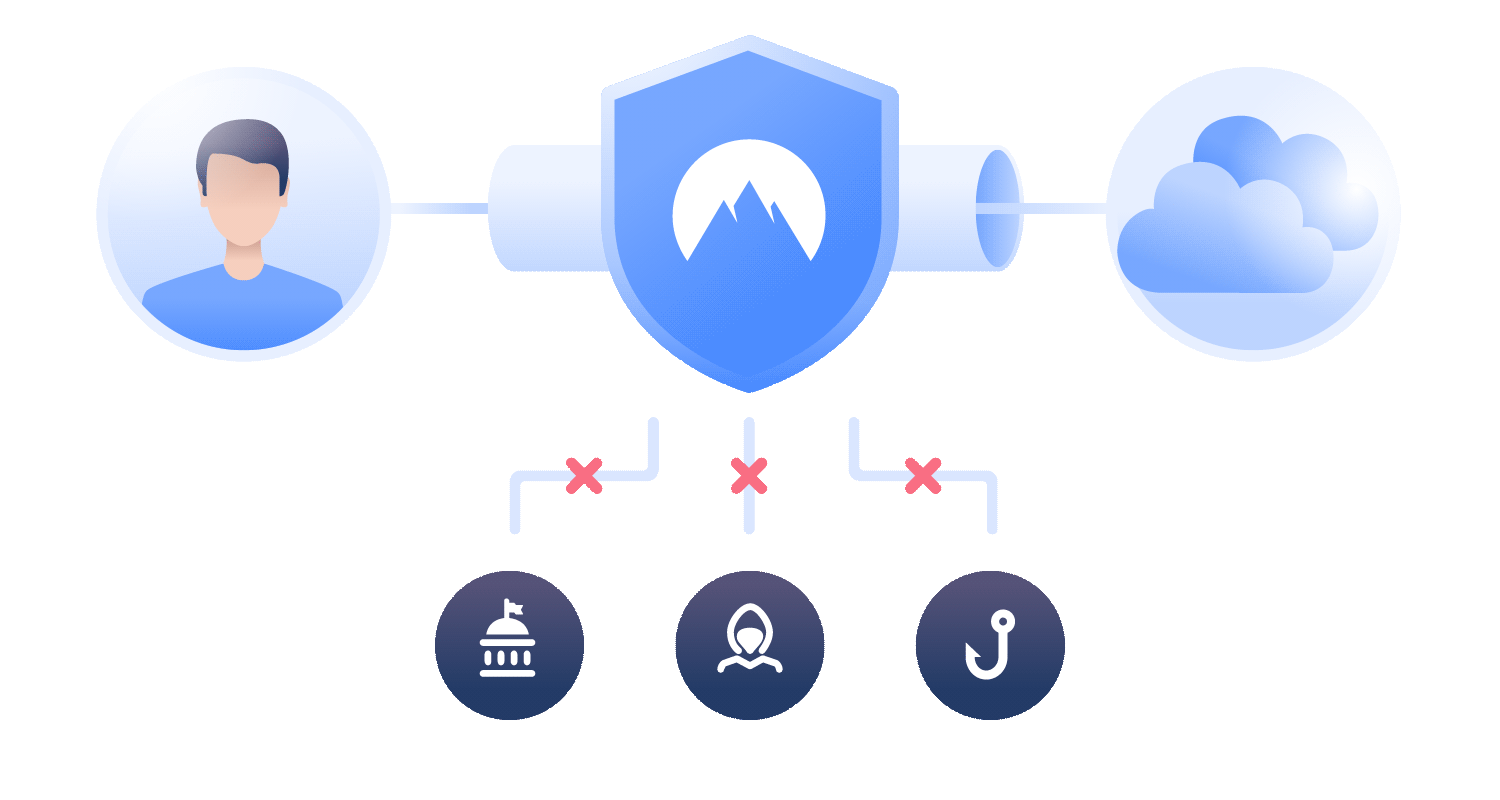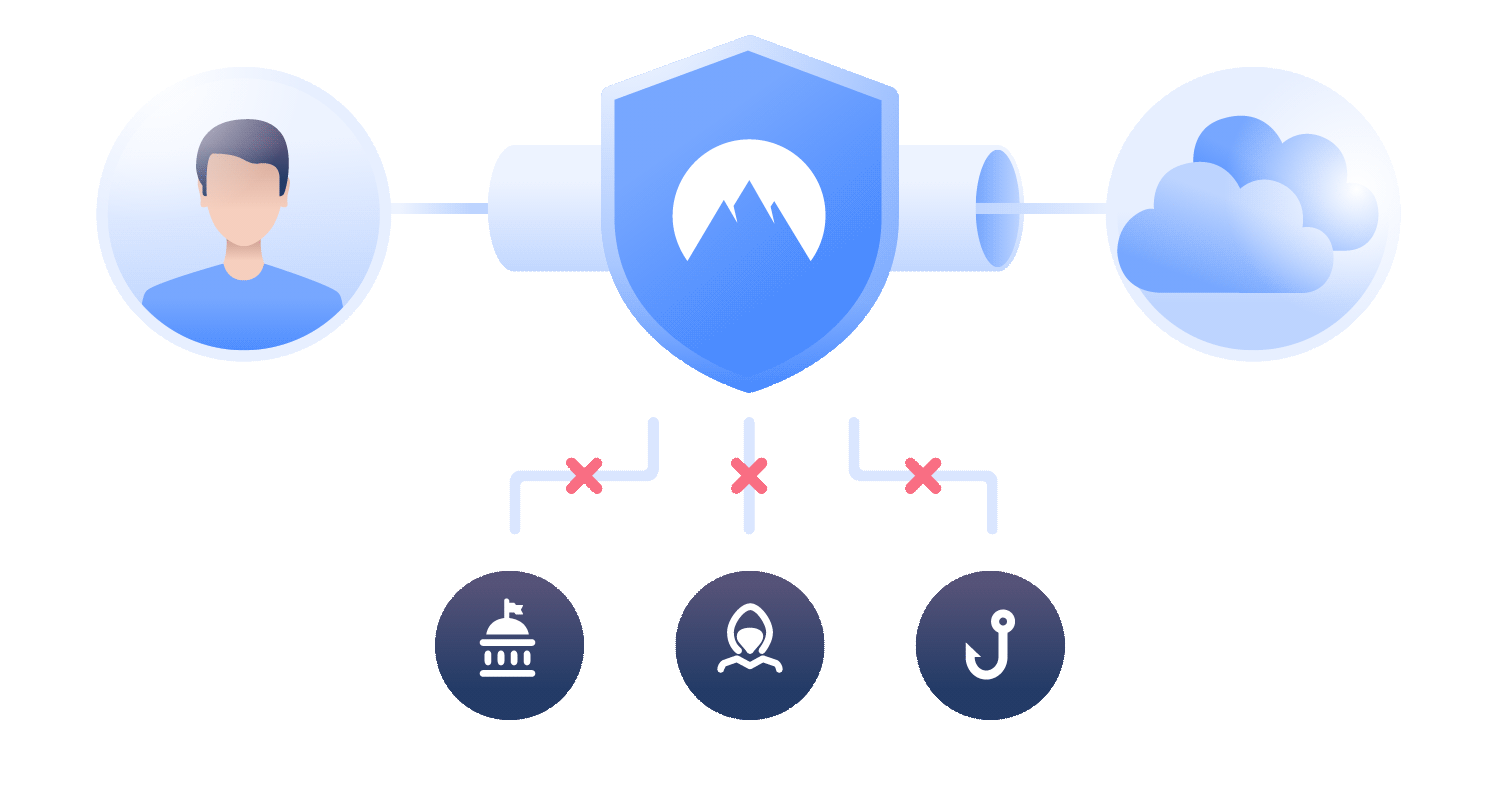
VPN Functionality
A VPN enhances this security by wrapping your data packets in an additional layer of encryption. When you use a VPN, your connection process changes significantly. After subscribing and installing a VPN app, each data packet is encrypted before it traverses through your Wi-Fi router and ISP.
The VPN server operates independently, meaning it does not log your local IP address, and the websites you access only see a random IP address from the VPN's server network. This ensures that your online activities remain private and unrecorded.
Chapter 2: Practical Applications of VPNs
In this video titled "What Is VPN & How Does It Work? | VPN Explained In 5 Minutes," you’ll gain a clear understanding of VPN functionality and its importance in safeguarding your online presence.
Another insightful video, "What is a VPN and How Does a VPN Work?" delves deeper into the mechanics of VPNs and their significance in today’s digital landscape.
Using VPNs Safely
Public Wi-Fi networks, such as those in airports or cafes, are notoriously insecure. Cybercriminals can easily set up fraudulent connections to intercept your data. While HTTPS can provide some protection, it doesn't guarantee complete safety.
Privacy Protection
Without a VPN, your ISP can track various aspects of your online activity, including timestamps, data volume, and connection duration. By utilizing a VPN, you can obscure this information, making it challenging for ISPs to monitor your online behavior.
Accessing Restricted Content
Some websites restrict access based on geographic location. VPNs offer a solution by allowing users to choose their virtual location, thus bypassing these restrictions.
VPN Limitations
It's crucial to choose a reliable VPN provider. A low-quality VPN may not offer significant advantages over your ISP, especially if it logs user data.
Legal Considerations
In certain jurisdictions, VPN services may be banned, leading to efforts to block their use. Some VPNs employ advanced techniques to evade detection, but this can affect connection speed.
Understanding Privacy vs. Anonymity
While a VPN can obscure your location, it doesn’t guarantee complete anonymity. Websites can still use methods like browser fingerprinting to track you.
Deep Packet Inspection
Some networks may employ deep packet inspection to analyze data packets for specific information, even if they are encrypted.
Operational Security
To mitigate risks, consider separating your public and private online activities. Some VPNs offer split tunneling, allowing you to control which traffic is routed through the VPN.
Conclusion
In summary, a VPN is an invaluable tool for enhancing your online privacy and security. With a modest monthly fee, you can access content globally, use public Wi-Fi securely, and protect your data from prying ISPs. However, it’s important to remember that a VPN is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to comprehensive online protection.